Decarbonisation and Energy Efficiency in Schools – Our Five-Step Guide
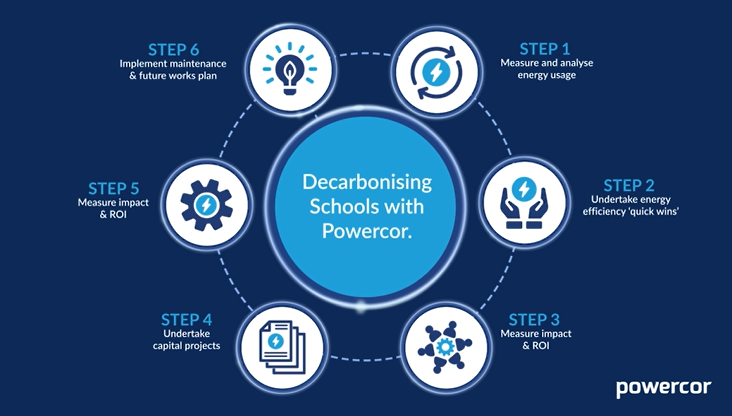
With growing pressure to cut carbon emissions and manage budgets more efficiently, energy efficiency in schools has become a top priority. Schools across the UK are actively seeking practical ways to reduce energy use and transition to greener operations. At Powercor, we understand that taking the first step can be the hardest. That’s why we’ve […]
Do Solar Panels Work on Cloudy Days?
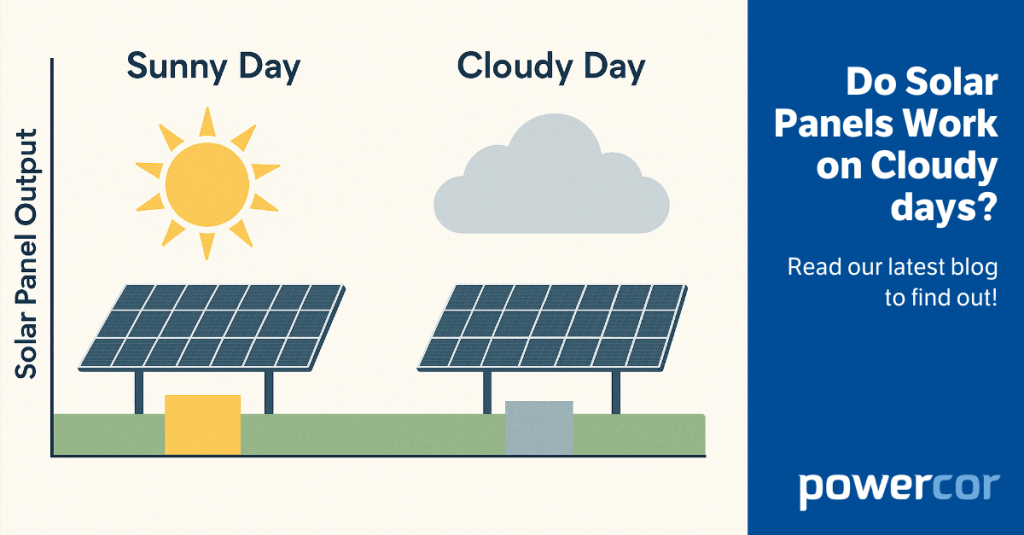
For those wondering ‘Do solar panels work on cloudy days?’, the simple answer is yes, they do! Solar panels operate by converting sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells don’t require direct sunlight; they can also utilise diffuse light that penetrates cloud cover. Even on cloudy days, there is sufficient ambient light for […]
Solving Solar Installation Issues in Surrey

Solar energy efficiency is becoming ever more popular in Surrey. With more homes and businesses making the switch, solar panels are now an important go-to green solution. Whether you’re looking to reduce your energy bills or reduce your carbon footprint, solar panels offer an attractive alternative to traditional energy sources. Yet, while there are many […]
Solar maintenance and insurance risk management

Installing solar photovoltaic (PV) panels in schools and businesses can often make sense as an investment in sustainability and energy efficiency. However, to ensure safety and compliance, insurance companies often set specific risk management and solar maintenance requirements. Whilst your site and installation will be unique, the following guidelines will go a long way to […]
ECA Video Series Launched in the House of Lords

We were recently delighted to partner with The Electrical Contractors’ Association (ECA) and Content With Purpose (CWP) to produce a forward-looking digital series exploring the transformative journey of electrification in the UK. Our role was to be part of a series of short films and interviews, telling the story of our apprentices and how Powercor […]
Energy efficiency and solar power in schools

As UK schools strive to enhance learning environments, it’s important for them to take the lead when it comes to the environment. Schools can make a substantial impact when it comes to energy efficiency and the use of solutions such as LED lighting and solar power will typically make a significant difference. With escalating concerns […]
10 key trends and statistics shaping the solar power industry in 2025

10 key trends and statistics shaping the solar power industry in 2025
The solar power industry is poised for significant advancements in 2025, driven by technological innovations, policy shifts, and increasing global demand for renewable energy. Here are ten key trends to watch:
1. Technological innovations in solar panels will increase in 2025
Advancements in solar panel technology are enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. Notably, Qcells has achieved a world record efficiency of 28.6% for a large-area silicon solar cell topped with perovskite, potentially reducing the space required for installations.
2. Solar energy storage capacity will continue to growth rapidly
The integration of energy storage systems is addressing the intermittency of solar power, improving grid stability, and enabling energy availability during peak demand or nighttime. This trend is particularly significant in the UK, where it is predicted that battery storage capacity will increase from the current level of 2.1GW to around 24GW by 2030.
3. Community and decentralised solar projects will expand
Community solar projects are expanding access to solar energy for those unable to install individual rooftop panels. In the UK, large-scale solar farms are becoming increasingly common, with over 1,336 operational sites and more planned, enhancing energy accessibility and contributing to decarbonization objectives.
4. In the UK, there will be significant investment in solar infrastructure
Major investments are propelling the solar industry forward. In the UK, the government’s clean energy plan will require investments in excess of £40 billion between 2025 and 2030 to drive renewable output, upskill workers and decarbonise the economy.
5. The corporates adoption of solar energy will continue
Businesses are increasingly adopting solar energy to meet sustainability goals and reduce operational costs. In the UK, companies like Marks & Spencer and Tesco entering into long-term solar power infrastructure projects, reflecting a broader corporate shift towards renewable energy sources.
6. Policy support and government targets will drive the solar industry in 2025
The UK government has laid out ambitious targets for solar energy capacity expansion as part of its plans and commitment to decarbonising the electricity system by 2030. The government’s Clean Power 2030 Action Plan—unveiled in December 2024—aims to increase solar capacity to approximately 45–47 gigawatts (GW) by 2030.
7. There will be further advances in solar panel recycling
As solar installations age, recycling technologies are developing to manage end-of-life panels, recovering valuable materials, and reducing environmental impact. In 2024, the global solar panel recycling market was worth US$ 1.87 billion in 2024 and is expected to exceed US$ 118.54 billion by 2037, expanding at a compound annual growth rate of over 37.6% during the period 2025 to 2037.
8. Artificial intelligence will play a key role in both solar energy management and usage
Artificial intelligence (AI) will both help to optimise solar energy production through improvements in supply-chain efficiency, but also drive up the demand for renewable energy via ever-expanding energy-hungry data centres.
9. Floating solar farms will continue their expansion
Floating solar farms, installed on bodies of water, are emerging as a solution to land constraints, offering efficient energy production without occupying valuable land resources. This innovative approach is gaining attention globally and could influence future solar projects. In fact, annual floating solar installations are expected to exceed 6 gigawatts (GW) by 2031. Moreover, the value of the global floating solar panel market was around US$ 35.6 million in 2022 and is projected to exceed US$ 180 billion by 2030.
10. We will see more integration of solar energy technology with Electric Vehicle (EV) Infrastructure
The convergence of solar power and EV charging infrastructure is set to play a pivotal role in the UK’s renewable energy landscape. Innovations such as solar carports are being developed to provide efficient charging solutions for electric vehicles, utilising solar panels to generate clean energy on-site. This integration supports the growing adoption of EVs and contributes to the decarbonisation of the transport sector.
How to choose the right solar panel installer for your business

The UK has seen a surge in solar panel installations as homeowners and businesses look to cut energy costs and reduce their carbon footprints. However, choosing the right solar panel installer is crucial to ensure that your investment delivers maximum benefits. A good installer can mean the difference between years of hassle-free energy savings and ongoing issues with underperforming equipment. This guide will help you with the process of finding a reliable and skilled solar panel installer in the UK.
The importance of a quality solar panel installer
Solar panels are a long-term investment, with systems designed to last 25 years or more. While the panels themselves are important, proper installation plays an equally significant role in their performance and longevity. A professional installer ensures that the system is safe, optimally positioned for sunlight, and integrated seamlessly with your home’s electrical setup. Poor installations, on the other hand, can lead to electrical failures, roof damage, or systems that underperform, resulting in lost savings and costly repairs.
Additionally, quality installation is essential for claiming warranties and adhering to insurance requirements. Manufacturers often stipulate that their equipment must be installed by certified professionals. By choosing a reputable installer, you safeguard your investment and gain peace of mind.
Finding installers in your area
The first step in your search is to identify installers operating in your region. In the UK, you’ll find a mix of national companies and local specialists. Local installers often provide more personalised service and are familiar with the specific challenges and regulations of your area. For instance, they may have insights into common weather-related considerations or local council requirements.
You can start by searching online for solar installation companies near you. Websites such as the Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS) directory are excellent resources. Word-of-mouth recommendations are another reliable option. Business associates, friends, or family members who might know of a quality installer can sometimes offer valuable insights and recommendations based on their experiences.
Checking certifications and qualifications
Certifications are a key indicator of an installer’s professionalism and expertise. The Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS) is the gold standard for solar installers. Any installer operating under the MCS has been vetted for technical competence and adherence to industry standards. Choosing an MCS-accredited installer is essential, as many financial incentives, such as the Smart Export Guarantee (SEG), require MCS certification.
Beyond MCS, you might also look for accreditation from organisations like the Solar Trade Association (STA). These endorsements demonstrate a commitment to customer service, ethical practices, and ongoing professional development. Additionally, verify that the installer holds public liability insurance and employer’s liability insurance, which protect both your property and the workers involved in the project.
Assessing experience and expertise
Experience is a crucial factor when choosing a solar panel installer. Ask potential installers about their track record and the number of installations they’ve completed. An experienced installer is more likely to have encountered a range of challenges and will know how to handle site-specific issues such as shading, unusual roof structures, or limited space.
Make sure the installer has experience with the type of system you’re planning to install. For example, if you’re considering battery storage or an integrated solar roof, confirm that they’ve handled similar projects before. Additionally, enquire about their familiarity with well-regarded manufacturers, like SolarEdge, and their understanding of local weather conditions, which can impact panel positioning and performance.
Reviewing portfolios of past work
A reputable installer should be able to provide examples of their previous work. Reviewing portfolios can give you an idea of the quality and style of their installations. Pay attention to projects that are similar to your own in terms of property type, roof size, or system complexity. You may also ask for references from previous clients to hear about their experiences firsthand.
Powercor has several examples of large and complex solar installations.
When reviewing past work, look for signs of attention to detail. Neat cable management, well-aligned panels, and robust mounting structures are all indicators of a high-quality installation. Don’t hesitate to ask questions about how they handled specific challenges or customised solutions for unique situations.
Reading reviews, testimonials and awards
Online reviews can provide valuable insights into an installer’s reliability and customer service. Websites like Trustpilot, Google Reviews, and Which? Trusted Traders are good places to start. Pay attention to comments about punctuality, communication, and how the installer dealt with any problems.
While reviews can be helpful, it’s important to approach them critically. Look for consistent patterns in feedback rather than focusing on isolated comments. Be cautious of reviews that seem overly positive or negative, as these might not always be genuine.
Look to see if the installer has won any industry awards. While this doesn’t guarantee quality workmanship, it does imply that the installer is established in their industry with a strong reputation.
Understanding pricing and quotes
The cost of solar panel installation in the UK varies depending on system size, complexity, and location. When comparing quotes, look beyond the bottom line. A good quote should break down costs for equipment, labour, and additional services such as scaffolding, permits, or monitoring systems. It should also clearly state any potential extra charges.
Beware of quotes that seem unusually low, as these may indicate subpar equipment or rushed installations. Conversely, higher quotes may reflect the quality of the equipment being used – so it’s always worth enquiring further.
Evaluating warranties and after-sales support
Warranties are a critical component of your solar investment. A trustworthy installer should offer guarantees on both equipment and workmanship. Equipment warranties typically range from 10 to 25 years, covering the solar panels, inverters, and batteries. Workmanship warranties, on the other hand, protect against installation-related issues and usually last for 1 to 10 years.
After-sales support is equally important. Ask the installer about their approach to maintenance and whether they offer annual servicing. Knowing you can rely on your installer for future support adds an extra layer of security.
Assessing customer service
The quality of customer service you receive during your initial interactions can be a good predictor of your overall experience. A professional installer should respond promptly to your enquiries, explain their processes clearly, and answer your questions patiently. Look for companies that prioritise transparency and are willing to discuss potential challenges upfront.
Compliance with local regulations
In the UK, solar panel installations must comply with local council regulations and building codes. A good installer will handle compliance on your behalf, ensuring that all necessary permits are obtained and that your system adheres to planning requirements. This is particularly important if you live in a listed building or a conservation area, where additional restrictions may apply.
Pre-installation site assessment
A thorough site assessment is a crucial step in the installation process. The installer should visit your property to evaluate factors like roof orientation, shading, and structural integrity. This allows them to design a customised system that maximises energy generation while addressing any potential challenges. Avoid installers who skip this step or offer quotes without visiting your property.
FAQs about finding a quality solar panel installer
• Why is MCS certification important in the UK? MCS certification is essential for ensuring that your installation meets industry standards. It’s also required for accessing financial incentives like the Smart Export Guarantee (SEG).
• How do I verify an installer’s credentials? You can check an installer’s MCS accreditation online or ask them to provide proof of certification and insurance.
• What is the typical cost of solar panels in the UK? The average cost for a domestic system ranges from £5,000 to £8,000, depending on the size and type of system. For businesses and schools, the roof space and system potential can be larger and the cost will rise proportionally
• What warranties should I expect? Look for equipment warranties lasting 10-25 years and workmanship warranties of at least 1-10 years.
• How long does the installation process take? This very much depends on the size and complexity of the site, but expect installation to take at least a week



